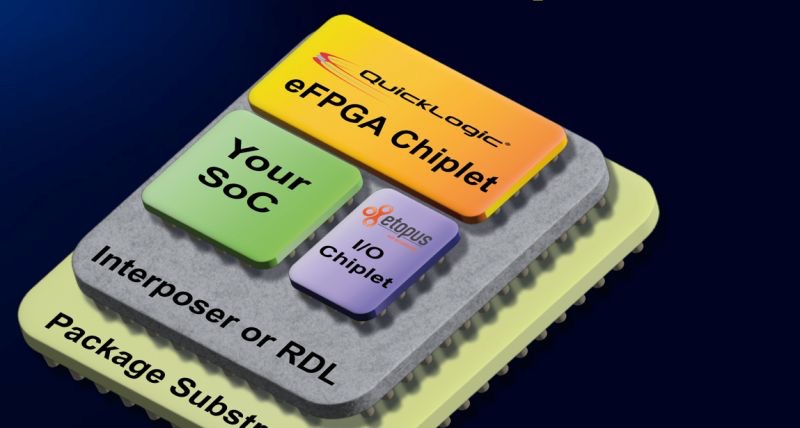
🚀 The Pizza Party: Imagine you’re hosting a pizza party, and you want to make the perfect pizza to satisfy all your guests’ tastes. Instead of trying to bake one gigantic pizza with every imaginable topping on it, you decide to make individual slices with different toppings. Each slice represents a specialized component, or chiplet, optimized for a specific function. For example, one slice might have pepperoni for the CPU processing power, another slice might have mushrooms for graphics processing, and yet another slice might have olives for memory storage. By baking these individual slices separately and then assembling them onto a common pizza crust, you can create a customized pizza that caters to everyone’s preferences. Some guests might want more CPU power, so they’ll take more pepperoni slices. Others might prioritize graphics performance, so they’ll go for more mushroom slices. And some might want a balance of both, so they’ll choose a variety of slices. 🚀 What is a chiplet? A chiplet is a discrete, modular component of an integrated circuit (IC) that performs a specific function, such as processing, memory, or input/output (I/O). Instead of fabricating an entire semiconductor device on a single monolithic die, chiplets allow designers to split the functionality into smaller, individual components that can be manufactured separately and then integrated onto a common substrate or package. 🚀 Why Chiplets are Important? 🔵 Manufacturing Efficiency: With the ever-shrinking process nodes and increasing complexity of IC designs, manufacturing entire chips on a single die becomes challenging and costly. Chiplets enable more efficient manufacturing by allowing each component to be fabricated using the most suitable process node and technology. 🔵 Performance Optimization: Chiplets allow designers to mix and match components optimized for specific functions. For example, a CPU chiplet can be combined with specialized chiplets for graphics processing, memory, or AI acceleration, allowing for better performance and power efficiency. 🔵 Time-to-Market: Developing a new semiconductor device from scratch can take years. By using chiplets, designers can leverage pre-existing, proven components, reducing development time and speeding up time-to-market for new products. 🔵 Scalability and Flexibility: Chiplets offer scalability and flexibility in design. Manufacturers can easily scale the number of chiplets in a package to meet different performance and cost requirements without having to redesign the entire system. Cost Reduction: Chiplets can lead to cost savings in several ways, including reduced development costs, lower manufacturing costs due to improved yield rates, and increased reusability of components across different products. A detailed post is in comments. For all semiconductors and AI related content, follow TechoVedas